MODULE 5 – Photosynthesis & Cell Respiration
May 7, 2009.
Refer to pp. 200-239 in the Prentice Hall Biology Book for background information during this module.
LESSON 5.01 – Chemical Equation for Photosynthesis
Standard: B1.f Students know usable energy is captured from sunlight by chloroplasts and is stored through the synthesis of sugar from carbon dioxide.
INTRODUCTION
In this lesson you will learn the equation for Photosynthesis and the process it represents.
INSTRUCTION
The key cellular process identified with energy production is photosynthesis. In the process of photosynthesis, plants use the energy of sunlight to convert water and carbon dioxide into high-energy carbohydrates—sugars and starches—and oxygen, a waste product. The investigations of many scientists have contributed to the current understanding of the process of photosynthesis.
The Photosynthesis Equation
Because photosynthesis usually produces 6-carbon sugars (C6H12O6) as the final product, the overall equation for photosynthesis can be shown as follows:

Example of Reactants & Products:

Like all chemical equations, this equation for photosynthesis shows reactants connected by plus signs on the left and products, also connected by plus signs, on the right. An arrow indicating the process or chemical change leads from the reactants to the products, and conditions necessary for the chemical reaction are written above the arrow. Note that the same kinds of atoms, and number of atoms, are found on both sides of the equation, but the kinds of compounds they form change.
Photosynthesis uses the energy of sunlight to convert water and carbon dioxide into high-energy sugars and oxygen. Plants then use the sugars to produce complex carbohydrates such as starches. Plants obtain carbon dioxide from the air or water in which they grow. The process of photosynthesis is shown in the figure below.
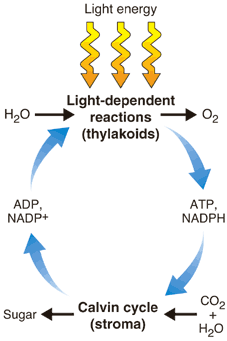
Photosynthesis is a series of reactions that uses light energy from the sun to convert water and carbon dioxide into sugars and oxygen.
Light and Pigments
Although the equation tells you that water and carbon dioxide are required for photosynthesis, it does not tell you how plants use these low-energy raw materials to produce high-energy sugars. To answer that question, you have to know how plants capture the energy of sunlight. In addition to water and carbon dioxide, photosynthesis requires light and chlorophyll, a molecule in chloroplasts.
Energy from the sun travels to Earth in the form of light. Sunlight, which your eyes perceive as “white” light, is actually a mixture of different wavelengths of light. Many of these wavelengths are visible to your eyes and make up what is known as the visible spectrum. Your eyes see the different wavelengths of the visible spectrum as different colors.
Plants gather the sun's energy with light-absorbing molecules called pigments. The plants' principal pigment is chlorophyll (KLAWR-uh-fil). There are two main types of chlorophyll: chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b.
As the figure below shows, chlorophyll absorbs light very well in the blue-violet and red regions of the visible spectrum. However, chlorophyll does not absorb light well in the green region of the spectrum. Green light is reflected by leaves, which is why plants look green. Plants also contain red and orange pigments such as carotene that absorb light in other regions of the spectrum.

Absorption of Light by Chlorophyll
Photosynthesis requires light and chlorophyll. In the graph above, notice how chlorophyll a absorbs light mostly in the blue-violet and red regions of the visible spectrum, whereas chlorophyll b absorbs light in the blue and red regions of the visible spectrum.
Because light is a form of energy, any compound that absorbs light also absorbs the energy from that light. When chlorophyll absorbs light, much of the energy is transferred directly to electrons in the chlorophyll molecule, raising the energy levels of these electrons. These high-energy electrons make photosynthesis work.
PRACTICE
- Take notes on the above information.
- Click here (http://videos.howstuffworks.com/hsw/12579-the-science-of-life-photosynthesis-video.htm) to watch a video about photosynthesis.
- Click here (http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yBfx3OcXS6A) to watch a video about photosynthesis.
ASSESSMENT
- Turn in your notes.
- Take the 5.01 Quiz.
Comments (0)
You don't have permission to comment on this page.